Zeta Potential
Molecular charge and nanoparticle zeta potential are core properties of a solute and a solvent, relevant to colloidal stability, chemical modifications and other key qualities.
What is Zeta Potential?
Zeta potential (ζ potential) is a critical parameter in colloidal systems, representing the electrokinetic potential at the slipping plane of a dispersed particle relative to the bulk fluid. It provides insight into the electric potential within the interfacial double layer that surrounds particles in suspension, particularly at the location where the mobile phase (dispersion medium) separates from the stationary fluid layer adhering to the particle surface.
This potential is typically expressed in millivolts (mV) and serves as an indirect measure of the net surface charge and the magnitude of electrostatic interactions within the system. The underlying mechanism governing zeta potential arises from the arrangement of counterions surrounding the charged particle surface. The inner Stern layer consists of ions that are strongly adsorbed to the particle surface, while the outer diffuse layer contains more loosely associated ions.
The boundary at which the ion distribution becomes sufficiently mobile to move with the particle is referred to as the slipping plane, and it is at this interface that the zeta potential is measured. As the particle moves, either through electrophoresis or sedimentation, the ions within this boundary remain associated with the particle, while ions beyond the slipping plane are left behind in the bulk solution.
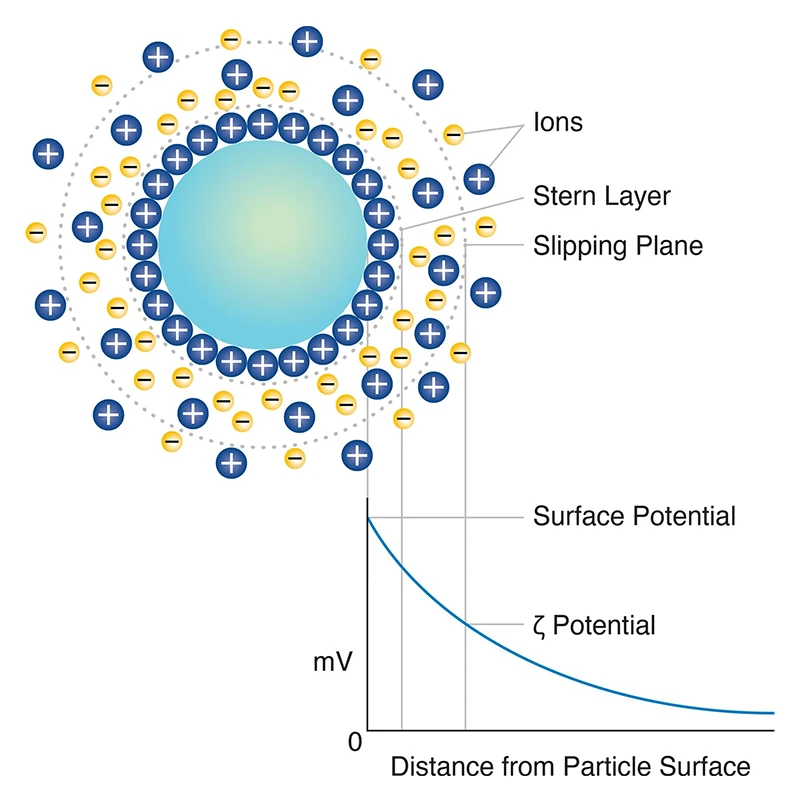
A figure showing zeta potential (ζ potential), the electrokinetic potential at the slipping plane of a dispersed particle.
Why is Zeta Potential important?
Zeta potential is a key factor in determining the stability of colloidal dispersions, as it directly influences the balance between attractive van der Waals forces and repulsive electrostatic forces. High zeta potential values (either positive or negative) indicate strong electrostatic repulsion between similarly charged particles, which prevents aggregation and maintains a stable dispersion.
Conversely, low zeta potential values suggest that the attractive forces dominate, increasing the likelihood of particle coagulation or flocculation, which compromises colloidal stability. The threshold for stability is typically defined as ±30 mV; systems with zeta potentials outside of this this threshold are generally considered stable, whereas those below it are prone to flocculation.

Images showing particles with high zeta potential are stable, while those with low zeta potential are unstable.
Stability behaviour of a colloid depending on zeta potential
| Magnitude of Zeta potential (mV) | Stability behavior |
|---|---|
| 0 to 5 | Rapid coagulation or flocculation |
| 10 to 30 | Incipient instability |
| 30 to 40 | Moderate stability |
| 40 to 60 | Good stability |
| > 60 | Excellent stability |
Barbosa JA, Abdelsadig MS, Conway BR, Merchant HA (December 2019). "Using zeta potential to study the ionisation behaviour of polymers employed in modified-release dosage forms and estimating their pKa". International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 1: 100024. doi:10.1016/j.ijpx.2019.100024. PMC 6733289. PMID 31517289.
Zeta Potential Applications
The ability to measure and control zeta potential is crucial for optimizing the stability of emulsions, suspensions, and dispersions across various industries. By understanding how pH, ionic strength, and temperature affect zeta potential, researchers can fine tune formulations to ensure long-term stability. This has significant applications in industries such as:
Biopharmaceutical
Zeta potential is used to assess the stability of drug delivery systems, such as liposomes and nanoparticles, ensuring proper dispersion and preventing aggregation in biotherapeutic formulations.
Cosmetics
It helps in optimizing the stability and texture of emulsions in skincare and beauty products, preventing separation or clumping of active ingredients in lotions, creams, and suspensions.

Food and Beverages
Zeta potential measurements are critical in controlling the stability of emulsions, dispersions, and colloidal suspensions in products like sauces, dressings, and beverages, ensuring homogeneity and preventing phase separation.

Paints, Coating, and Additive Manufacturing
Zeta potential is used to maintain the dispersion of pigments and additives like rheological modifiers, improving the uniformity and adhesion properties in paints, inks, and 3D printing materials.

Water Treatment
It is applied to monitor and enhance the efficiency of coagulation and flocculation processes, helping to optimize particle removal and improve water clarity in municipal and industrial treatment systems.

How to measure Zeta Potential?
Electrophoretic Light Scattering (ELS) is a technique used to measure the zeta potential of particles in suspension by observing their movement in an applied electric field. When an electric field is applied, charged particles in the suspension move toward the electrode of opposite charge. The speed at which these particles move, known as their electrophoretic mobility, is directly related to their zeta potential.
The ELS process involves shining a laser through the particle suspension. As the particles move, they scatter the light, and the Doppler shift of this scattered light (a change in frequency due to the particles' motion) is detected. By analyzing the frequency shift, the electrophoretic mobility of the particles is calculated, which can then be used to determine the zeta potential using the Smoluchowski equation (for large particles) or the Hückel equation (for small particles in low-conductivity media).
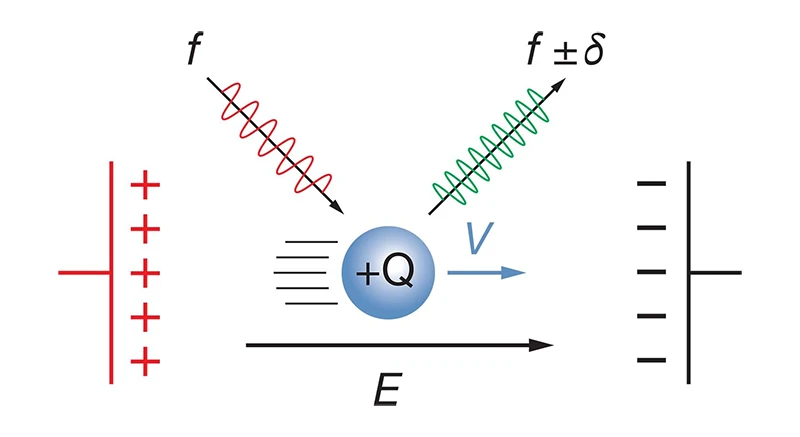
Illustration of laser doppler effect: light scattered from a particle in an electric field is frequency-shifted.
Zeta Potential Analyzer
Our newest generation zeta potential analyzer, the DynaPro™ ZetaStar™ instrument, performs simultaneous dynamic and electrophoretic light scattering (DLS/ELS) measurements, manually with microcuvettes, or automatically, via an autosampler and flow cell.
The ZetaStar instrument delivers both increased sensitivity and up to 10x faster DLS/ELS measurements using up to 10x less samples compared to previous generation zeta potential analyzer.

DynaPro ZetaStar Instrument
Walk-up or automated measurements of DLS, SLS and ELS.



