Conformation
Light scattering determines branching in polymers and other measures of sub-micron shape or structure, entirely in solution.
Introduction
Smaller than the wavelength of visible light, it is notoriously difficult to determine the shape, structure or conformation of macromolecules and nanoparticles. While imaging techniques such as AFM and cryoTEM can in some cases provide detailed information, they require significant alterations to native solution conditions with deposition on a surface, and measure a very small, often unrepresentative ensemble. Light scattering offers non-invasive determination of conformation, in solution, over large and representative ensembles.
The use of triple-detection GPC combining multi-angle static light scattering (MALS), differential viscometry (dVI) or dynamic light scattering (DLS), and differential refractometry (dRI), independently or in combination, provides quantitative analysis of:
- Branching ratio in polymers and dendrites
- The shape of protein aggregates or amyloid fibrils
- Empty or filled carrier nanoparticles
Branching Ratio
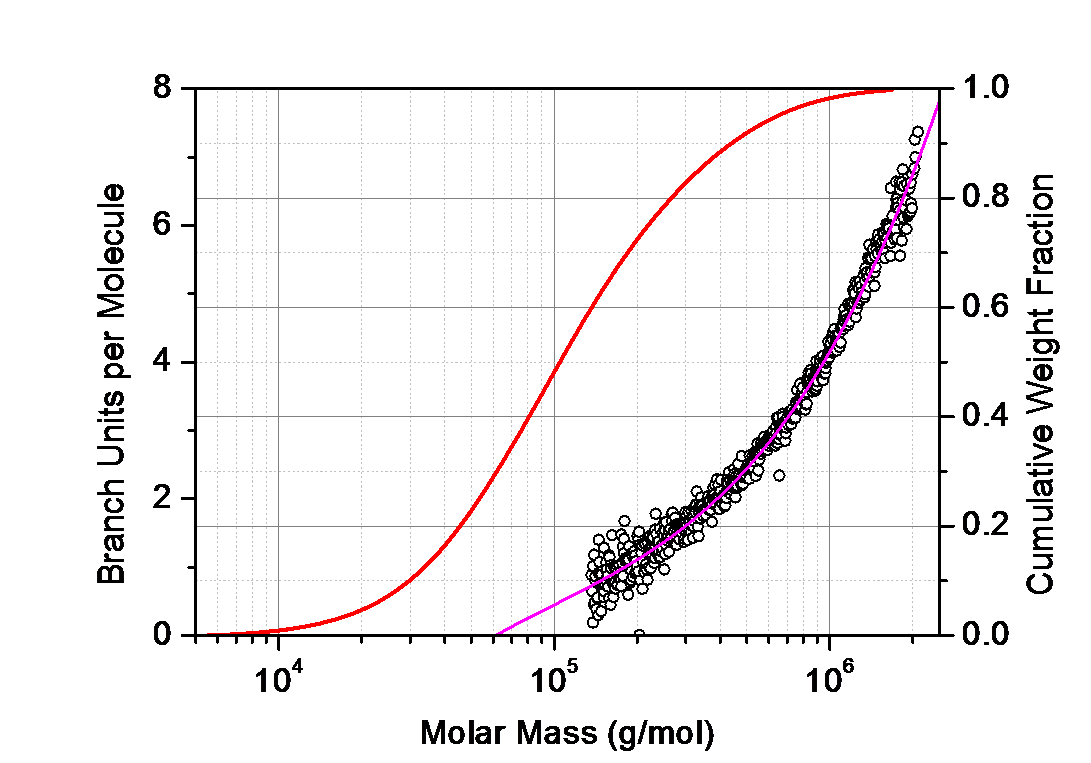
Important properties of synthetic polymers such as stiffness, viscosity and solubility are governed by the branching ratio g. As outlined in the white paper 'Branching Revealed: Characterizing Molecular Structure in Synthetic and Natural Polymers by Multi-Angle Light Scattering' by Dr. Stepan Podzimek, the branching ratio is most reliably determined from the slope v of the log-log plot of the rms radius Rg vs molar mass Mw. Since MALS determines both parameters - simultaneously and independently - downstream of a size-based separation technique such as SEC-MALS or FFF-MALS, it is the ideal technique for this purpose, as long as molecules are larger than about 10 nm in radius.
For smaller molecules, the hydrodynamic radius Rh as determined by differential viscometry or online DLS may be substituted for Rg. The addition of a ViscoStar™ differential viscometer to a MALS system introduces the parallel capability for dVI analysis to determine branching and the Mark-Houwink parameter.
Shape Factor
For macromolecular assemblies besides branched polymers, the log-log plot of Rg vs. Mw is indicative of shape. Increasing values of the slope v progress from spherical, to random coil, to linear conformations of polymers and aggregates. For example, amorphous protein aggregates are distinguished from amyloid fibrils by the value of v, which is in the range of spherical/random coil for amorphous aggregates but much closer to the value expected for a linear arrangement in the case of amyloid fibrils.
Similar information is obtained from the shape factor, ρ = Rg/Rh, for each macromolecular size fraction. The theoretical shape factor of ellipsoids, often taken to represent macromolecules and their assemblies or aggregates, is well known as a function of semi-axis ratio. Hence MALS with simultaneous, integrated DLS by means of the WyattQELS™ module is an independent and orthogonal method to confirm the shape of an assembly or nanoparticle.
When the analyte is known to have a particular shape, the shape factor provides structural information. For example, since liposomes are always spherical, the shape factor ρ clearly differentiates between empty liposomes and those filled with a substance such as a drug compound.
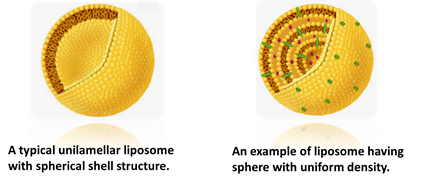
ρ = ~1.00
ρ = ~0.77
Resources
Selected References
Ahmad, I. A. H.; Striegel, A. M. Influence of second virial coefficient and persistence length on dilute solution polymer conformation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 1515-1521.
Peng, Y.; Zhang, L. Characterization of a polysaccharide-protein complex from Ganoderma tsugae mycelium by size-exclusion chromatography combined with laser light scattering. J. Biochem. Bioph. Meth. 2003, 56, 243-252.
Striegel, A. M. Architecture on the mechanochemical degradation of macromolecules. J. Biochem. Bioph. Meth. 2003, 56, 117-139.
Tarazona, M. P; Saiz, E. Combination of SEC/MALS experimental procedures and theoretical analysis for studying the solution properties of macromolecules. J. Biochem. Bioph. Meth. 2003, 56, 95-116.
Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Perrier, S.; Zhao, Y. Facile synthesis of hyperbranched and star-shaped polymers by RAFT polymerization based on a polymerizable trithiocarbonate. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2034-2049.
Instrumentation for Conformation Analyses
MALS Detectors

DAWN™ - The most sensitive MALS detector available, anywhere. Incorporates detectors at 18 angles to determine molar masses from 200 Da to 1 GDa and radii from 10 – 500 nm.
- Standard option: ambient temperature
- Heated/cooled option: -15 °C to +150 °C
- High-temperature option: ambient to +210 °C
The DAWN offers special options to handle fluorescent samples: fluorescence-blocking filters and an infrared, 785 nm laser.
miniDAWN™ - Second only to the DAWN in sensitivity. Incorporates detectors at 3 angles to determine molar masses from 200 Da to 10 MDa and radii from 10 – 50 nm. Ambient only.
microDAWN™ - The first MALS detector for UHPLC, with interdetector dispersion as low as 1.5 µL. Incorporates detectors at 3 angles to determine molar masses from 200 Da to 20 MDa and radii from 10 – 50 nm. Ambient only.
Viscometer

ViscoStar™ - A highly sensitive, on-line differential viscometer used in conjunction with SEC-MALS to determine the size and conformation of all types of biopolymers, synthetic polymers and even proteins and peptides.
The ViscoStar incorporates multiple novel technologies to provide the highest sensitivity, stability and solvent compatibility of any available viscometer for GPC. Its ease-of-use and serviceability make it the perfect companion for Wyatt's DAWN™ light scattering and Optilab™ refractive index detectors. Temperature controlled from 4 °C to 70 °C.
microViscoStar™ - Similar to the ViscoStar but designed specifically for use with UHPLC/APC.
Refractive Index Detectors
Optilab™ - A unique on-line differential refractometer for measuring concentration of any macromolecule, regardless of chromophores. Temperature controlled from 4°C to 65°C. The high-concentration option accommodates protein concentration up to 180 mg/mL.
microOptilab™ - The first RI detector specifically designed for use with UHPLC systems. Compatible with all UHPLC systems.
Field-Flow Fractionation Systems

Field-flow fractionation performs versatile separations of macromolecules and nanoparticles ranging from 1 to 1000 nm in diameter and beyond. FFF-MALS-DLS is the ideal means for obtaining distributions of molar mass and size, nanoparticle concentration and extended characterization of conformation and conjugate content.
Eclipse™ - An FFF instrument offering superior performance, reliability and user experience. Supports the Dilution Control Module™ for enhanced sensitivity, and the SEC switching option for sharing the system between FFF and SEC separation modes.
Mobility™ EAF4 system - An add-on to an Eclipse which performs electrical/asymmetrical-flow FFF for determining charge and zeta potential distributions.
Eclipse Channels - The Eclipse offers a wide selection of separation channels and membranes to accommodate a variety of analytical and even semi-preparative tasks.
Dynamic Light Scattering Detectors

WyattQELS™ - A dynamic light scattering (DLS) module which integrates into a DAWN, miniDAWN or microDAWN MALS detector to provide simultaneous DLS measurements in the same scattering volume.
DynaPro™ NanoStar™ - With sample volumes as small as 1.25 µL and temperature control spanning -15 °C to +150 °C, the NanoStar goes above and beyond traditional cuvette-based DLS instruments: it offers an optimized static light scattering detector in parallel to the DLS detection system which may be used for rapid assessment of conformation. The NanoStar does double duty as an online DLS detector by installing its optical collection fiber into a Wyatt MALS detector.
Software
ASTRA™ - Our comprehensive software solution for MALS analysis in chromatography, AF4 or batch mode. ASTRA is available in a 21 CFR Part 11 compliant version and offers additional options such as particle analysis and a research database. Provides multiple types of conformation analysis including conformation plots, Mark-Houwink-Sakurada parameters and shape factor.
DYNAMICS™ - Software for batch DLS measurements in the DynaPro instruments, as well as molar mass and A2 in the NanoStar and DynaPro Plate Reader. Calculates size and size distributions, and derives parameters such as the melting temperature Tm, the aggregation onset temperature Tagg and the diffusion interaction parameter kD. Calculates axial ratio based on diffusion coefficient, specific volume and molar mass. DYNAMICS is available in standard and 21 CFR Part 11 compliant versions.
